EN ISO 11612

REQUIREMENTS FOR FABRIC AND MATERIALS FOR PROTECTIVE CLOTHING FOR HEAT AND FLAMES
The EN ISO 11612 standard analyses protective properties of garments, their materials (protective fabrics) and accessories when presented with heat and flames. In addition, this standard analyses whether resistance, shrinkage and useful life meet minimum levels. All this is certified in official ILAC-MRA laboratories.

EN ISO 11612 CERTIFICATION REQUIREMENTS
DESCRIPTION
MINIMUM COMPLIANCE VALUES
ISO 17493
Clothing and equipment for protection against heat – Test method for convective heat resistance using a hot air circulating oven.
180ºC (260ºC optional)
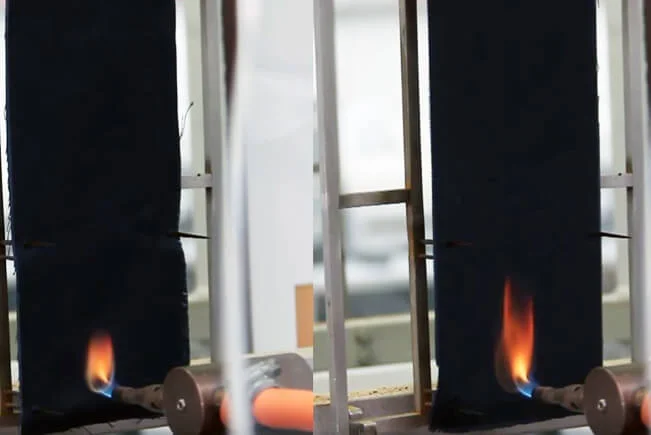
ISO 15025
Protective clothing – Protection against flames – Method of test for limited flame spread.
A1 or A2
ISO 9151
Protective clothing for heat and flame – Determination of convective heat transmission on exposure to flame
B1
ISO 6942
Protective clothing – Protection against heat and fire – Determination of heat transmission on exposure to a source of radiant heat
C1
ISO 9185
Protective clothing – Assessment of resistance of materials to molten metal splash.
–
ISO 12127-1
Protective clothing for heat and flames – Determination of contact heat transmission through protective clothing or constituent materials – Part 1: Contact heat produced by heating cylinder.
F1
ISO 5077
Textiles – Determination of dimensional change in washing and drying.
3% woven fabric 5% knit fabric
ISO 13934-1
Textiles – Tensile properties of fabrics – Part 1: Determination of maximum force and elongation of maximum force using the strip method.
Min 300 N
ISO 13937-2
Textiles – Tensile properties of fabrics – Part 2: Determination of maximum force using the tear method.
Min 10 N
ISO 13938-1
Textiles – Bursting properties of fabrics – Part 1: Hydraulic method for determination of bursting strength and bursting distension.
minus 100 kPa (for a test area of 50 cm2) or 200 kPa (for a test area of 7 cm2).
ISO 13938-2
Textiles – Bursting properties of fabrics – Part 2: Pneumatic method for determination of bursting strength and bursting distension.
minus 100 kPa (for a test area of 50 cm2) or 200 kPa (for a test area of 7 cm2).